Are Th1 cells lymphocytes?
Table des matières
- Are Th1 cells lymphocytes?
- What is the role of Th1?
- What are Th1 vs Th2?
- What are Th2 lymphocytes?
- What is Th1 in immunology?
- What cells do Th1 cells activate?
- What does Th1 mean in immunology?
- How do Th1 cells work?
- What is the Th1 response?
- Are Th2 anti inflammatory?
- What is the difference between Th1 and Th2 lymphocytes?
- What cytokines are produced by Th1 and Th2 cells?
- What is the pathophysiology of th1-dominated responses?
- What are Th1 and Th2 phenomena?
Are Th1 cells lymphocytes?
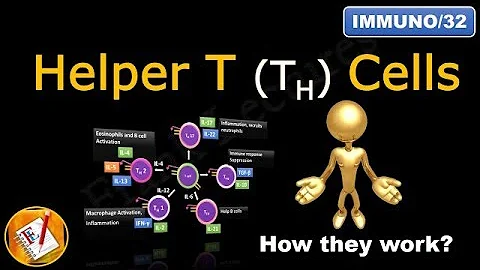
Th1 Cells. ... Th1 lymphocytes are controlled by the transcription factor T-bet and characterized by their expression of IL-2, IL-12, TNF-α, and IFN-γ. Th1 cells function to activate macrophages and neutrophils; and are critical for host defense against intracellular pathogens such as M. tuberculosis.
What is the role of Th1?
The main effector functions of Th1 cells are in cell-mediated immunity and inflammation, including the activation of cytolytic and other effector functions of other immune cells such as macrophages, B cells, and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs).
What are Th1 vs Th2?
Th1 and Th2 cells play an important role in immunity. Th1 cells stimulate cellular immune response, participate in the inhibition of macrophage activation and stimulate B cells to produce IgM, IgG1. Th2 stimulates humoral immune response, promotes B cell proliferation and induces antibody production (IL-4).
What are Th2 lymphocytes?
T helper type 2 (Th2) cells are a distinct lineage of CD4+ effector T cell that secretes IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13, and IL-17E/IL-25. These cells are required for humoral immunity and play an important role in coordinating the immune response to large extracellular pathogens.
What is Th1 in immunology?
T helper type 1 (Th1) cells are a lineage of CD4+ effector T cell that promotes cell-mediated immune responses and is required for host defense against intracellular viral and bacterial pathogens. Th1 cells secrete IFN-gamma, IL-2, IL-10, and TNF-alpha/beta.
What cells do Th1 cells activate?
Th1 cells activate macrophages, NK cells, and CD8+ T cells to combat intracellular pathogens. Th1 cells also stimulate immunoglobulin class switching in B cells for the production of immunoglobulin G2a (IgG2a) antibodies that optimize clearance of viruses and extracellular bacteria (see Chapter 20).
What does Th1 mean in immunology?
T helper type 1 (Th1) cells are a lineage of CD4+ effector T cell that promotes cell-mediated immune responses and is required for host defense against intracellular viral and bacterial pathogens. Th1 cells secrete IFN-gamma, IL-2, IL-10, and TNF-alpha/beta.
How do Th1 cells work?
Th1 cells secrete IFN-γ, a signature cytokine that activates macrophages and DCs and thereby enhances their ability to kill intracellular microbes and to present antigens to T lymphocytes. Th1 cells can also secrete tumor necrosis factor (TNF), lymphotoxin, and IL-2, which contribute to antimicrobial defense as well.
What is the Th1 response?
Th1-type cytokines tend to produce the proinflammatory responses responsible for killing intracellular parasites and for perpetuating autoimmune responses. Interferon gamma is the main Th1 cytokine.
Are Th2 anti inflammatory?
In summary, our data show that activation of Th2 responses inhibits inflammatory arthritis. Mechanistically, IL-4/IL-13-STAT6 signalling pathway induces macrophage polarization into anti-inflammatory macrophages into the joints. In addition, eosinophils are activated and further contribute to the resolution of disease.
What is the difference between Th1 and Th2 lymphocytes?
- Human type 1 helper (Th1), but not type 2 helper (Th2), cells produce interleukin-2 (IL-2), gamma-interferon (IFN-gamma), and tumor necrosis factor-beta, whereas Th2, but not T … Human Th1 and Th2 lymphocytes: their role in the pathophysiology of atopy
What cytokines are produced by Th1 and Th2 cells?
- Other cytokines, such as IL-3, IL-6, GM-CSF, or TNF-alpha, are produced by both Th1 and Th2 cells. Th0 cells, a third Th subset, show combined production of Th1- and Th2-type cytokines.
What is the pathophysiology of th1-dominated responses?
- Both environmental and genetic factors act in concert to determine the Th1 or Th2 polarization. Further, Th1-dominated responses are involved in the pathogenesis of organ-specific autoimmune disorders, Crohn's disease, sarcoidosis, acute kidney allograft rejection, and some unexplained recurrent abortions.
What are Th1 and Th2 phenomena?
- Both of these states are chiefly viewed as Th2 phenomena (to reduce the risk of miscarriage, a strong Th2 response is necessary to modify the Th1 cellular response in utero). The fetus can switch on an immune response early in pregnancy, and because pregnancy is chiefly a Th2 situation, babies tend to be born with Th2 biased immune responses.













